PowerHub Home Assistant Integrations
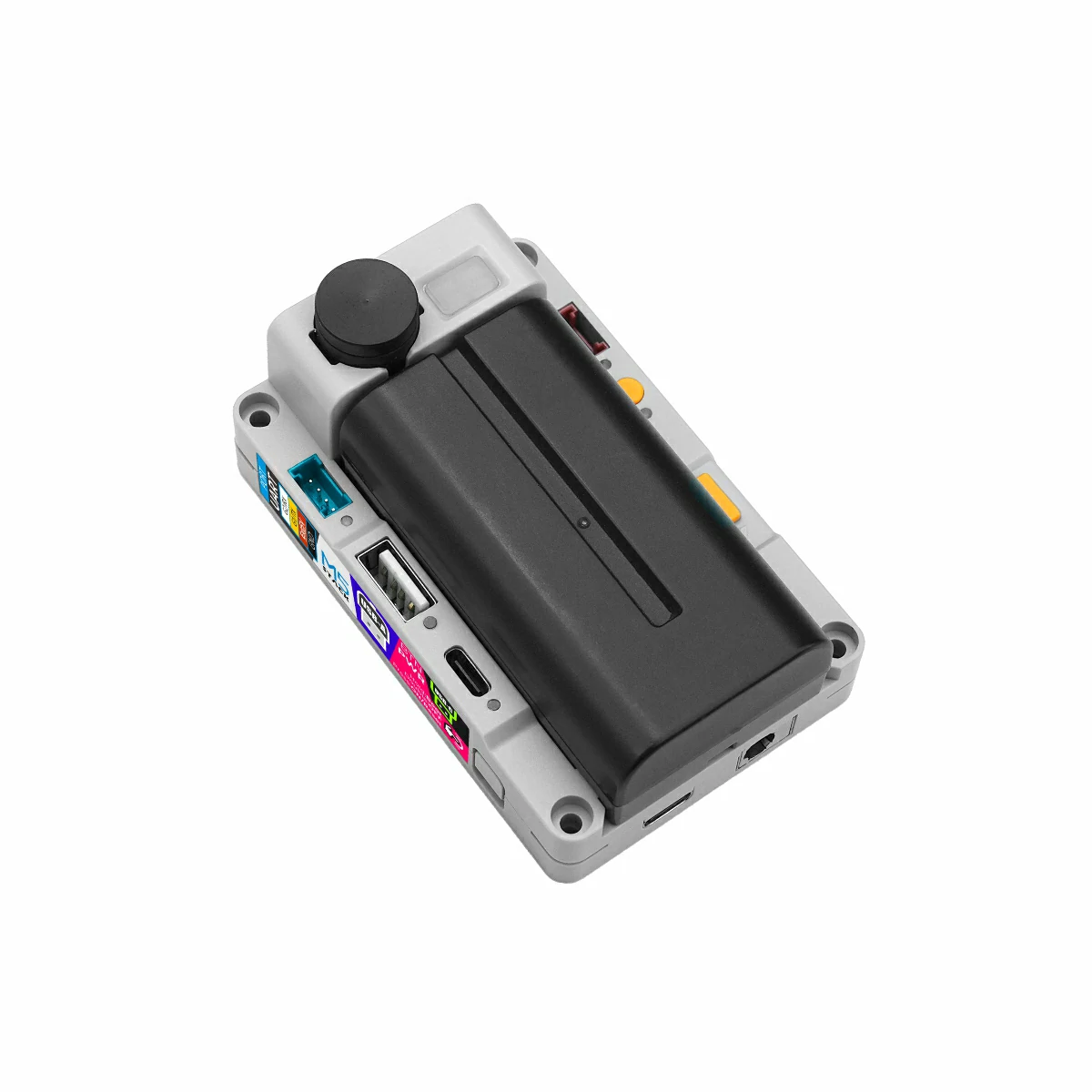

PowerHub is a programmable controller integrating multi-channel power management. It adopts the ESP32-S3-WROOM-1U-N16R8 main control module equipped with a dual-core Xtensa LX7 processor (up to 240MHz), supporting 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, with 16MB Flash and 8MB PSRAM onboard. A built-in STM32G031G8U6 coprocessor, combined with multiple INA226 voltage/current detection ICs and electronic switch design, enables precise management of power states for multiple expansion interfaces, achieving accurate power consumption control and providing low-power wake-up functionality for the whole device.
This article shows how to integrate PowerHub into your Home Assistant
Preparation
- Home Assistant host
- Install and enable ESPHome Builder in Home Assistant
2025.11.2. If you run into compile/upload issues, consider switching ESPHome to this version.Open ESPHome Builder in Home Assistant and create an empty configuration file.
Click the
NEW DEVICEbutton in the lower-right corner.In the dialog, click
CONTINUE.
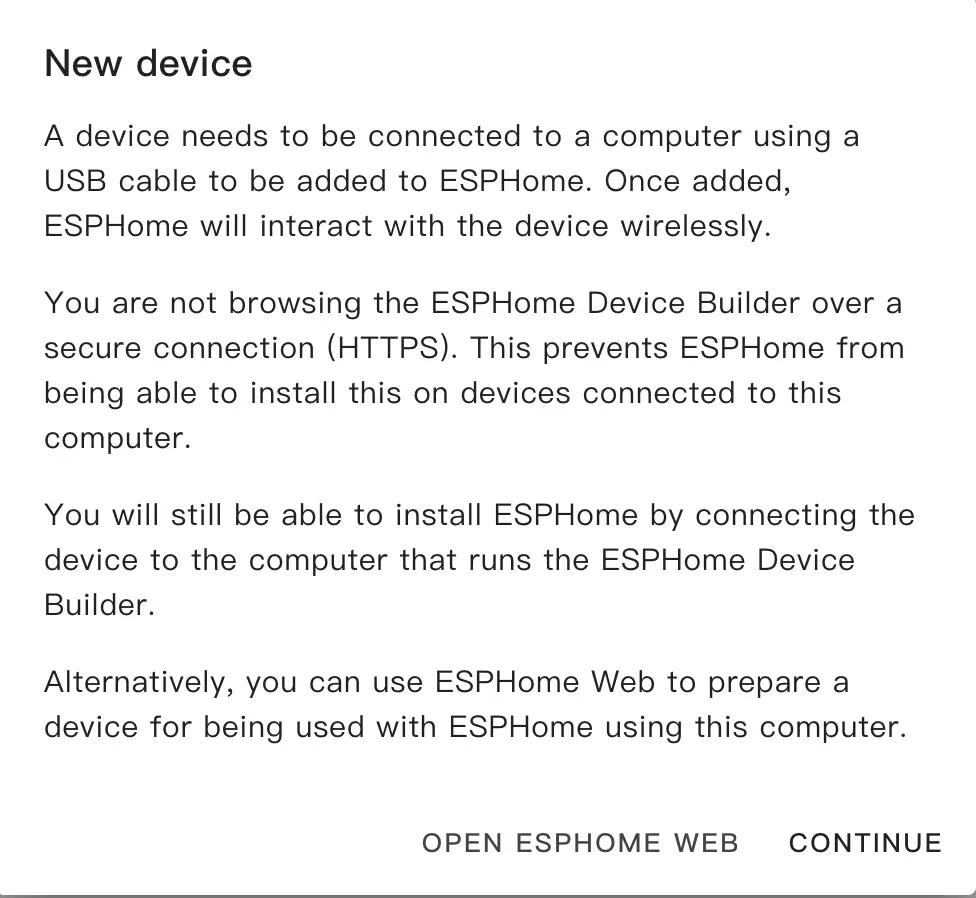
- Select
Empty Configuration.
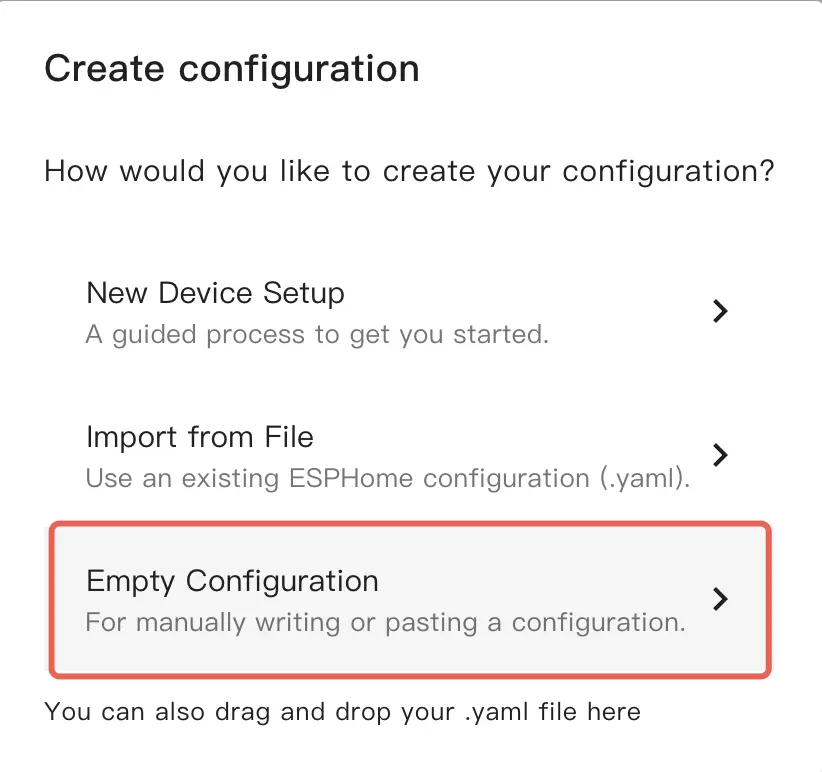
- (Optional) Enter a filename.
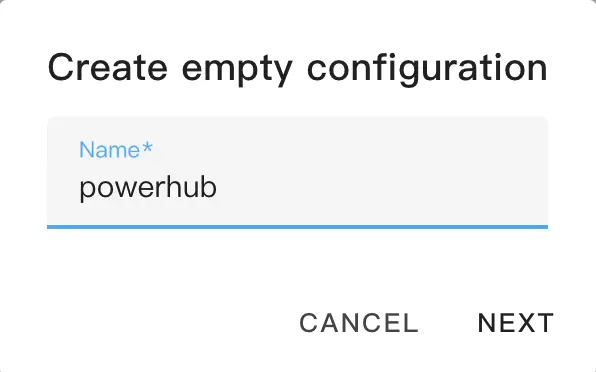
- Click
EDITon the newly created configuration file.
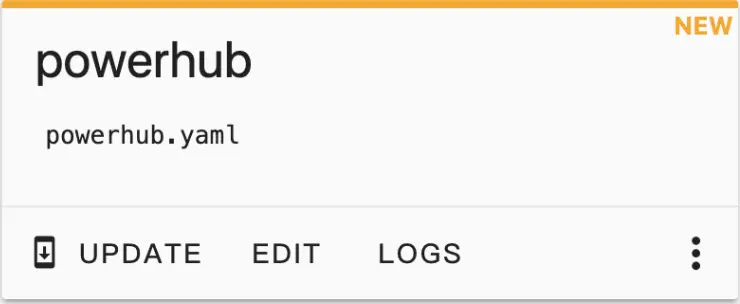
Then copy the contents of configurations.yaml into the configuration file.
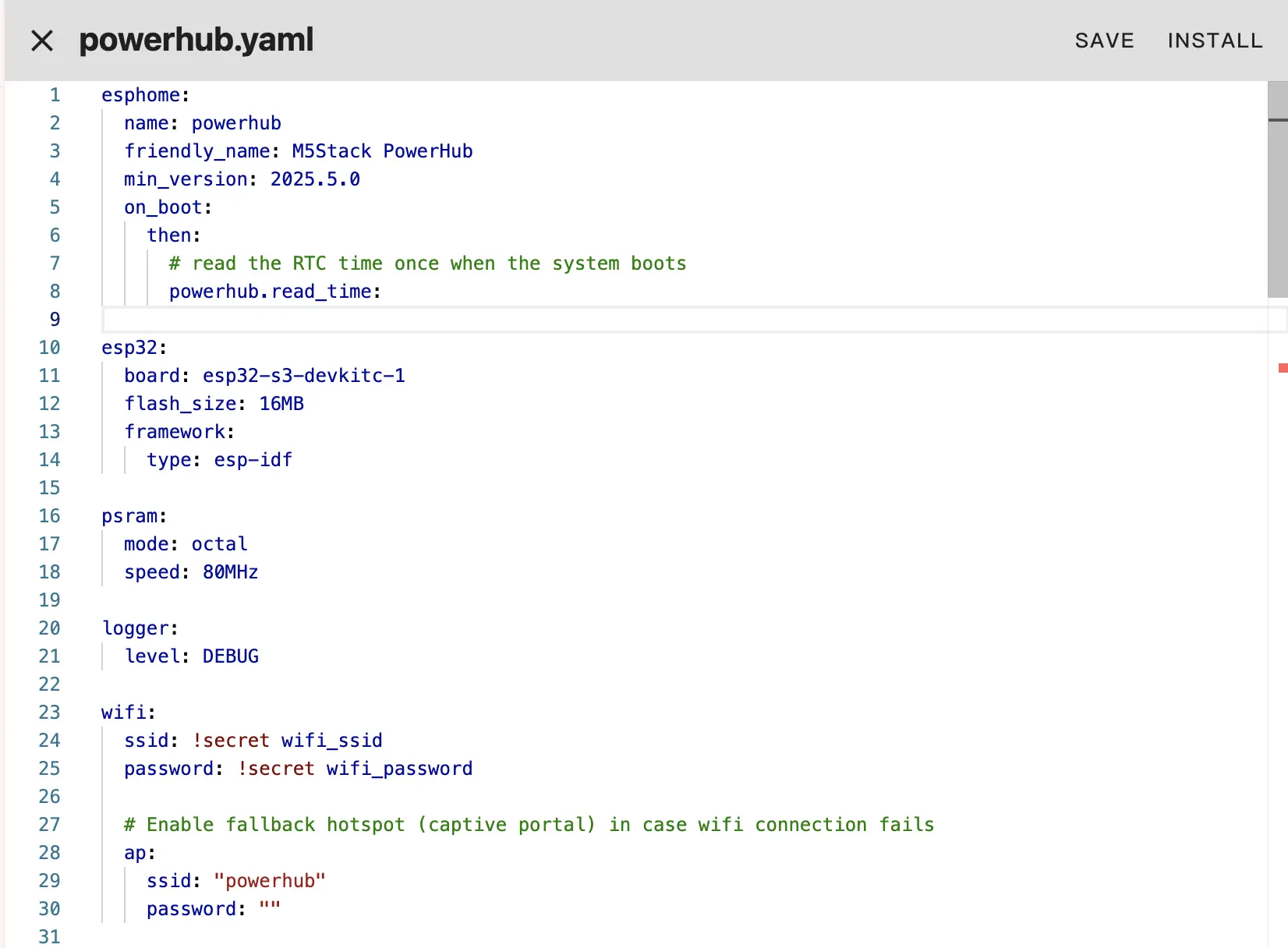
Change network configuration or API info as needed, for example creating an API Encryption Key for authentication:
api:
encryption:
key: "Your_Encryption_Key"Or change the time zone setting:
timezone: Europe/LondonReplace with the correct time zone:
timezone: Asia/ShanghaiNext, click SAVE and then INSTALL in the upper right, and choose Manual download.
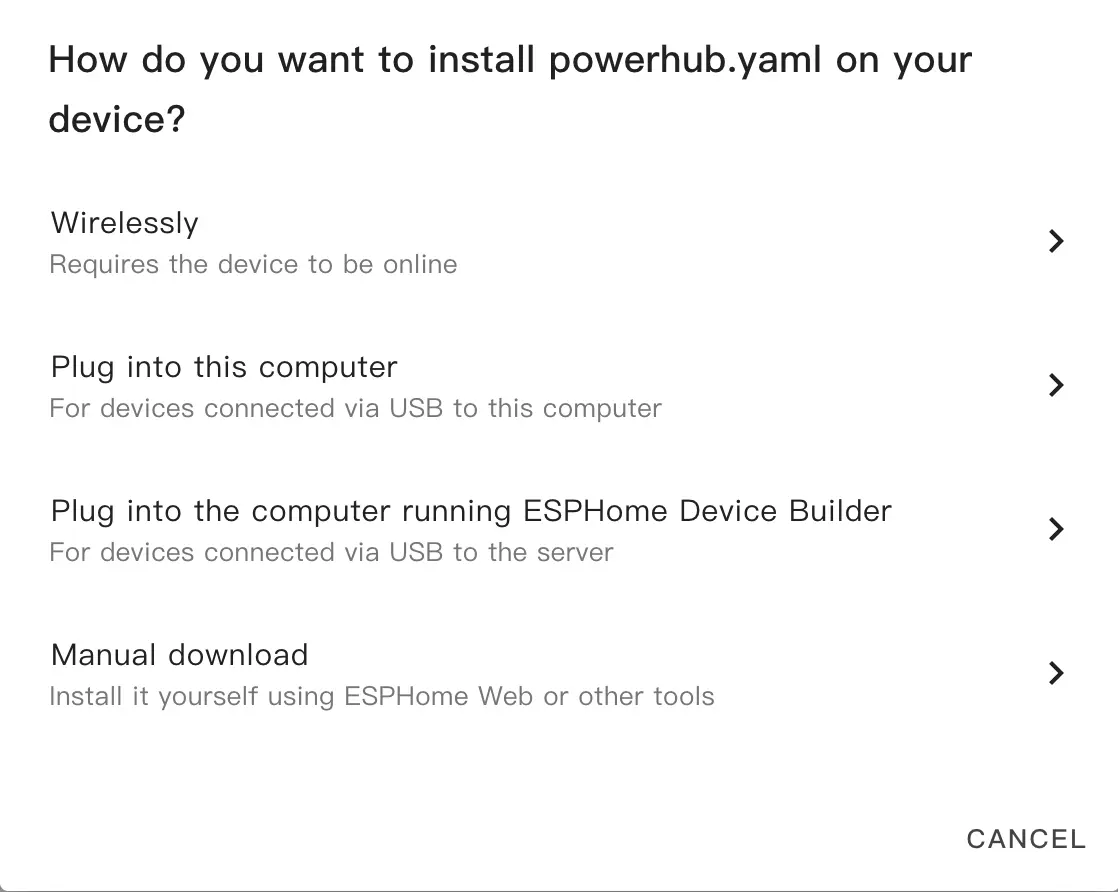
Code will be generated and the project compiled.
When compilation finishes, choose Factory format to download the firmware.
Upload firmware
Open ESPHome Web in a browser and upload the firmware.
Connect the PowerHub to your host with a USB-C cable, click CONNECT, and select the device.
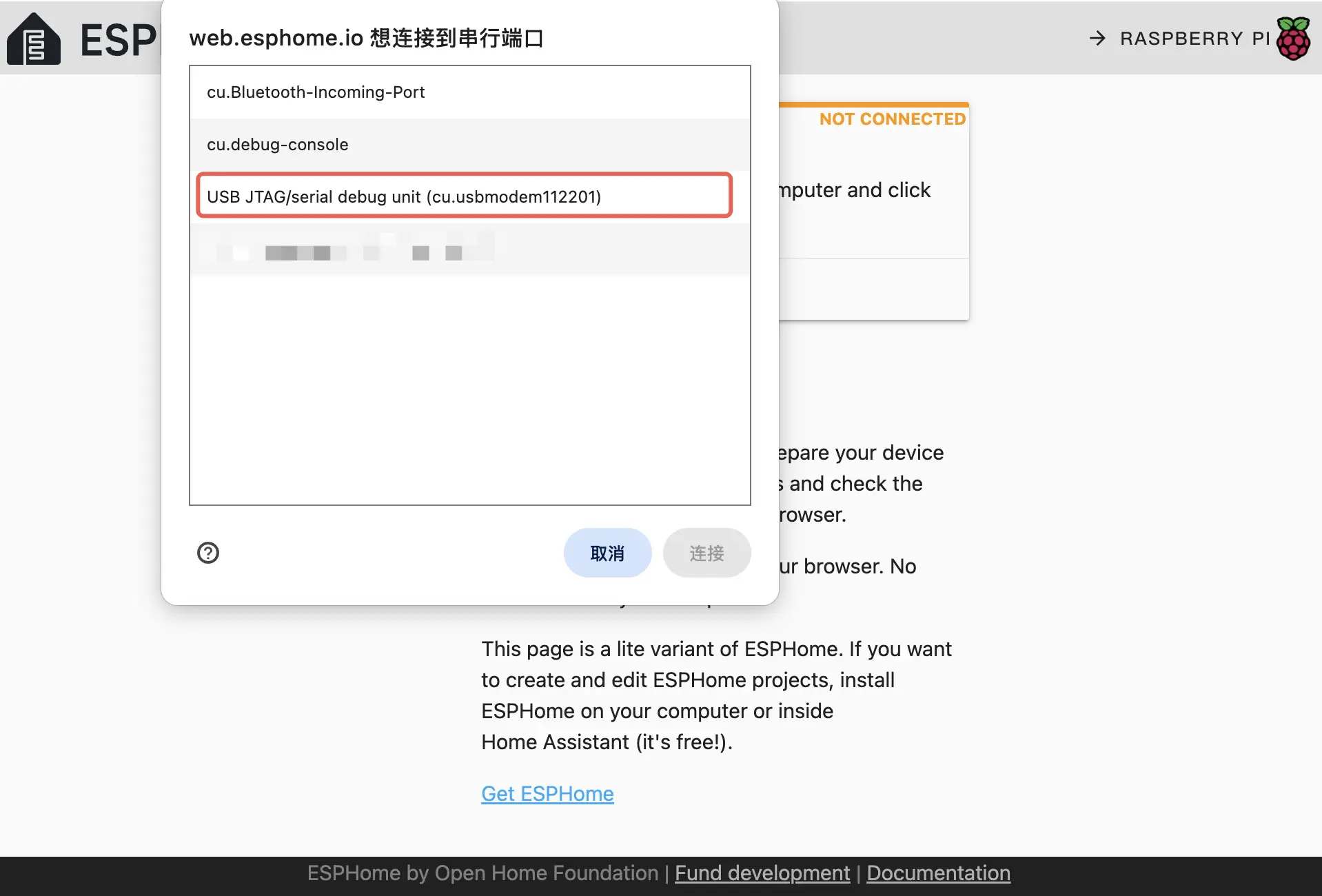
Then click INSTALL, choose the previously downloaded firmware, and click INSTALL again to flash the device.

After flashing completes, the device will reset automatically.
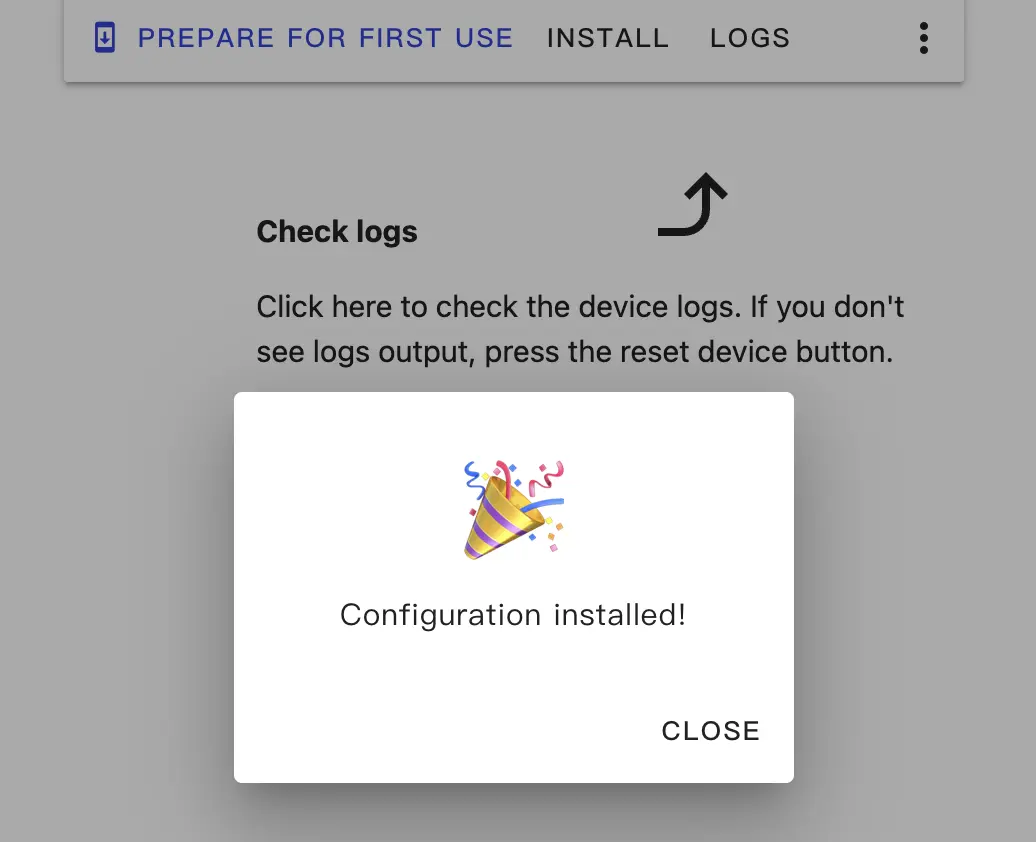
Add device to Home Assistant
When the device restarts, it will connect to the configured network. Under normal conditions it can be discovered in Settings -> Devices & services.

Click Add to integrate PowerHub into Home Assistant. If you set an API Encryption Key earlier, you may need to enter it here.
Example PowerHub dashboard:
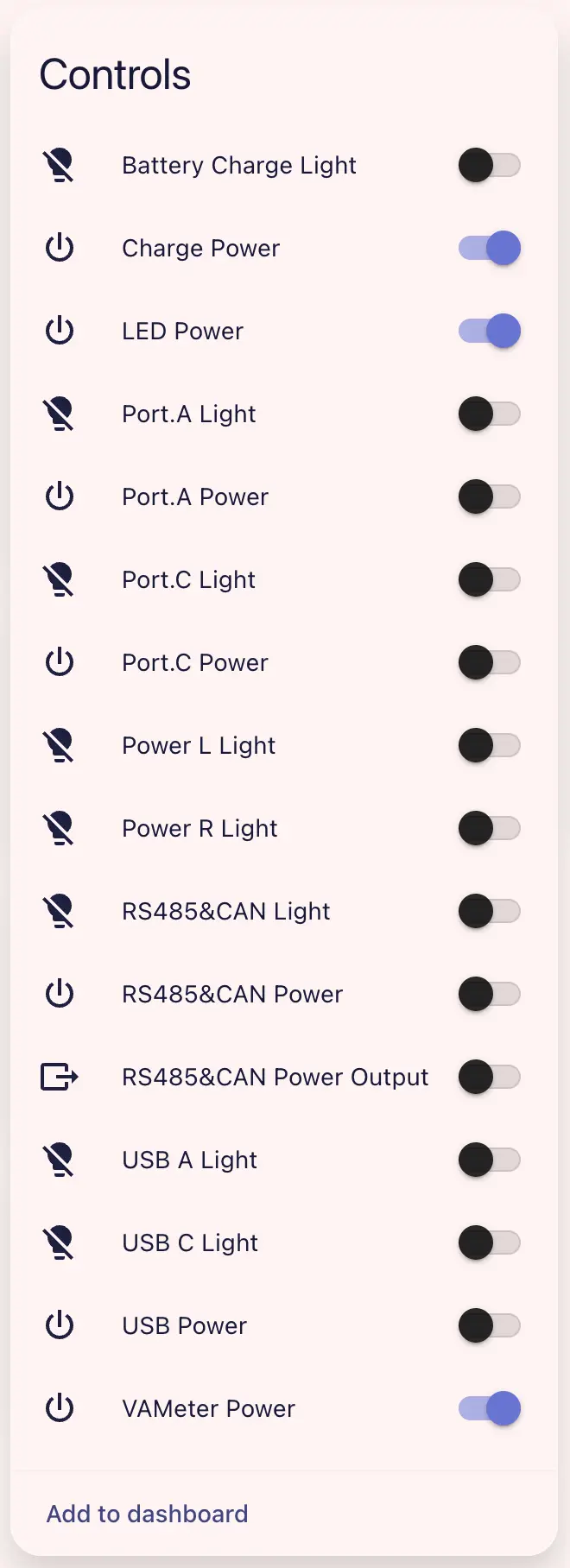
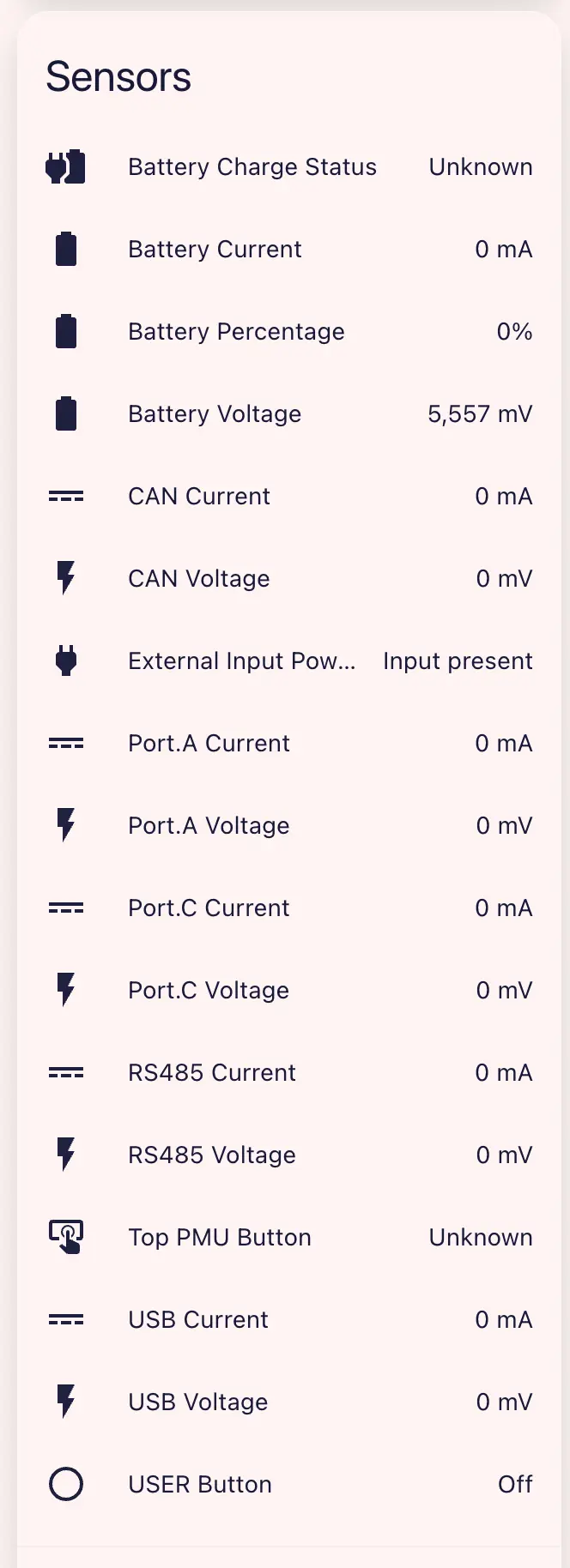
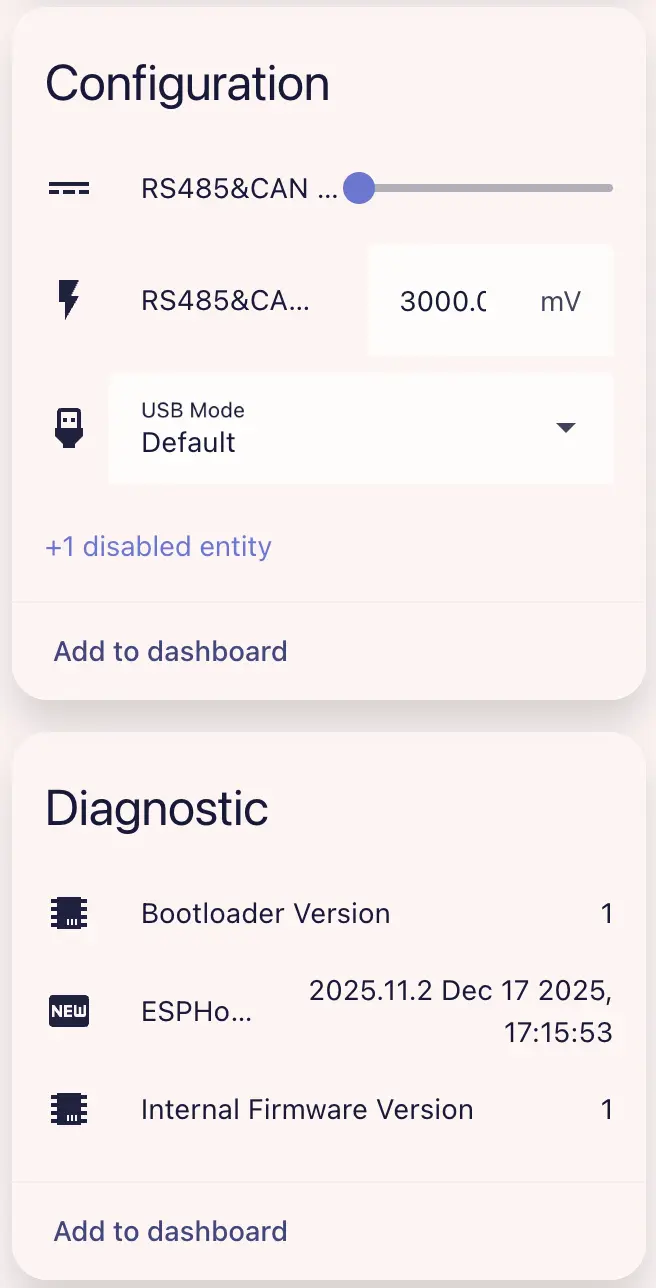
You can control each light or power output via light/power switches, set USB operating mode via the dropdown, and set RS485 & CAN output voltage/current limits (turn on RS485 & CAN Power Output).
Component/Hub
The I2C is required to configure the device.
- The device offered a RS485 and CAN interface, if you wish to use RS485 and CAN interface, additional configurations for components like Modbus Controller and CAN Bus are required.
- You can set the set the USB mode for USB Type A or USB Type C on the device, if you wish to operate the USB interfaces for communications, USB Host Interface and TinyUSB may required.
# Example configuration entry
powerhub:Configuration variables
- id (Optional, ID): Specify an ID for PowerHub component.
- update_interval (Optional, Time): The interval to check the sensor. Set to never to disable updates. Defaults to
10s.
Binary Sensor
Binary Sensor on powerhub was mainly to detect whether the top PMU button is pressed.
binary_sensor:
- platform: powerhub
id: powerhub_binary_sensor
button:
name: "Top PMU Button"Configuration variables
- powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
- button (Optional): Detect if the top PMU button (rectangular shape) is pressed. All options from Binary Sensor.
Sensor
Sensors on powerhub report various of voltage/current and other measurements.
sensor:
- platform: powerhub
battery_voltage:
name: "Battery Voltage"
id: bat_volt_sensor
battery_current:
name: "Battery Current"
id: bat_curr_sensor
battery_level:
name: "Battery Percentage"
id: bat_level_sensor
grove_red_voltage:
name: "Port.A Voltage"
id: grove_red_volt_sensor
grove_red_current:
name: "Port.A Current"
id: grove_red_curr_sensor
grove_blue_voltage:
name: "Port.C Voltage"
id: grove_blue_volt_sensor
grove_blue_current:
name: "Port.C Current"
id: grove_blue_curr_sensor
can_voltage:
name: "CAN Voltage"
id: can_volt_sensor
can_current:
name: "CAN Current"
id: can_curr_sensor
rs485_voltage:
name: "RS485 Voltage"
id: rs485_volt_sensor
rs485_current:
name: "RS485 Current"
id: rs485_curr_sensor
usb_voltage:
name: "USB Voltage"
id: usb_volt_sensor
usb_current:
name: "USB Current"
id: usb_curr_sensorConfiguration variables
- battery_voltage (Optional): The voltage of the battery. All options from Sensor
- battery_current (Optional): The current of the battery. All options from Sensor
- battery_level (Optional): Report battery level in percentage. All options from Sensor
- grove_red_voltage (Optional): The voltage of grove red ( Port.A ) channel. All options from Sensor
- grove_red_current (Optional): The current of grove red ( Port.A ) channel. All options from Sensor
- grove_blue_voltage (Optional): The voltage of grove blue ( Port.C ) channel. All options from Sensor
- grove_blue_current (Optional): The current of grove blue ( Port.C ) channel. All options from Sensor
- can_voltage (Optional): The voltage of CAN interface. All options from Sensor
- can_current (Optional): The current of CAN interface. All options from Sensor
- rs485_voltage (Optional): The voltage of RS485 interface. All options from Sensor
- rs485_current (Optional): The current of RS485 interface. All options from Sensor
- usb_voltage (Optional): The voltage of USB interface. All options from Sensor
- usb_current (Optional): The current of USB interface. All options from Sensor
- powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
VAMeter Power switch and corresponding power channel switch are enabled, and corresponding load has been connected (like a battery, a USB device etc).Text Sensor
Text sensors on powerhub report the power status in text format, as well as the internal firmware/bootloader version of the device.
text_sensor:
- platform: powerhub
charge_status:
name: "Battery Charge Status"
id: bat_charge_status_text_sensor
vin_status:
name: "External Input Power Status"
id: ext_vin_status_text_sensor
firmware_ver:
name: "Internal Firmware Version"
id: int_firm_ver_text_sensor
bootloader_ver:
name: "Bootloader Version"
id: boot_ver_text_sensorConfiguration variables
- charge_status (Optional): Detect if the battery is charging. All options from Text Sensor.
- vin_status (Optional): Detect if external input power is present. All options from Text Sensor.
- firmware_ver (Optional): Report the internal firmware version of the device. All options from Text Sensor.
- bootloader_ver (Optional): Bootloader version of the device. All options from Text Sensor.
- powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
Switch
The powerhub switches allow you to enable or disable power channels from the front end.
switch:
- platform: powerhub
led_pwr:
name: "LED Power"
id: led_pwr_switch
usb_pwr:
name: "USB Power"
id: usb_pwr_switch
grove_red_pwr:
name: "Port.A Power"
id: grove_red_pwr_switch
grove_blue_pwr:
name: "Port.C Power"
id: grove_blue_pwr_switch
rs485_can_pwr:
name: "RS485&CAN Power"
id: rs485_can_pwr_switch
vameter_pwr:
name: "VAMeter Power"
id: vameter_pwr_switch
charge_pwr:
name: "Charge Power"
id: charge_pwr_switch
rs485_can_direction:
name: "RS485&CAN Power Output"
id: rs485_can_direction_switchConfiguration variables
- led_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the LED power. Defaults to
true. All options from Switch - usb_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the USB power. All options from Switch
- grove_red_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the Port.A (grove red) power. All options from Switch
- grove_blue_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the Port.C (grove blue) power. All options from Switch
- rs485_can_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the RS485 & CAN power. All options from Switch
- vameter_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the VAMeter power. Defaults to
trueAll options from Switch - charge_pwr (Optional): Turn on/off the charge power. Defaults to
trueAll options from Switch - rs485_can_direction (Optional): Control the RS485 & CAN power output direction. Turn on to enable the output. All options from Switch
- powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
Select
powerhub select allows you to change the USB mode of the USB Type A or USB Type C interface.
select:
- platform: powerhub
usb_mode:
name: "USB Mode"
id: usb_mode_selectConfiguration variables
- usb_mode (Optional): Set the host/device mode of the USB Type A or USB Type C port. Note that you can't set both port to USB host mode.
Defaults to device mode. Values can be
Default,Host for USB-CorHost for USB-A. All options from Select. - powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
Number
The number settings can be used to set the RS485 & CAN interface's output voltage and current limit.
number:
- platform: powerhub
rs485_can_output_voltage:
name: "RS485&CAN Output Voltage"
rs485_can_current_limit:
name: "RS485&CAN Output Current Limit"Configuration variables
- rs485_can_output_voltage (Optional): Set the output voltage of the RS485 & CAN interface. Defaults to
3000mV. The switchrs485_can_directionneeds to be enabled for this to take effect. All options from Number. - rs485_can_current_limit (Optional): Set the output current limit of the RS485 & CAN interface. Defaults to
12mA. The switchrs485_can_directionneeds to be enabled for this to take effect. All options from Number. - powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
Light
Each power channel on powerhub is equipped with a status RGB LED to indicate the power status.
light:
- platform: powerhub
usb_c_rgb:
name: "USB C Light"
usb_a_rgb:
name: "USB A Light"
grove_blue_rgb:
name: "Port.C Light"
grove_red_rgb:
name: "Port.A Light"
rs485_can_rgb:
name: "RS485&CAN Light"
bat_charge_rgb:
name: "Battery Charge Light"
pwr_l_rgb:
name: "Power L Light"
pwr_r_rgb:
name: "Power R Light"Configuration variables
- usb_c_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED under the USB Type C interface. All other options from Light.
- usb_a_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED under the USB Type A interface. All other options from Light.
- grove_blue_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED under the Port.C (grove blue) interface. All other options from Light.
- grove_red_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED under the Port.A (grove red) interface. All other options from Light.
- rs485_can_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED under the RS485 & CAN interface. All other options from Light.
- bat_charge_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED for battery charge status. This LED is located under the yellow round button. All other options from Light.
- pwr_l_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED for left power indicator. This LED is located inside the left half of the Top PMU button (rectangular shape). All other options from Light.
- pwr_r_rgb (Optional): Turn on/off RGB LED for right power indicator. This LED is located inside the right half of the Top PMU button (rectangular shape). All other options from Light.
- powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
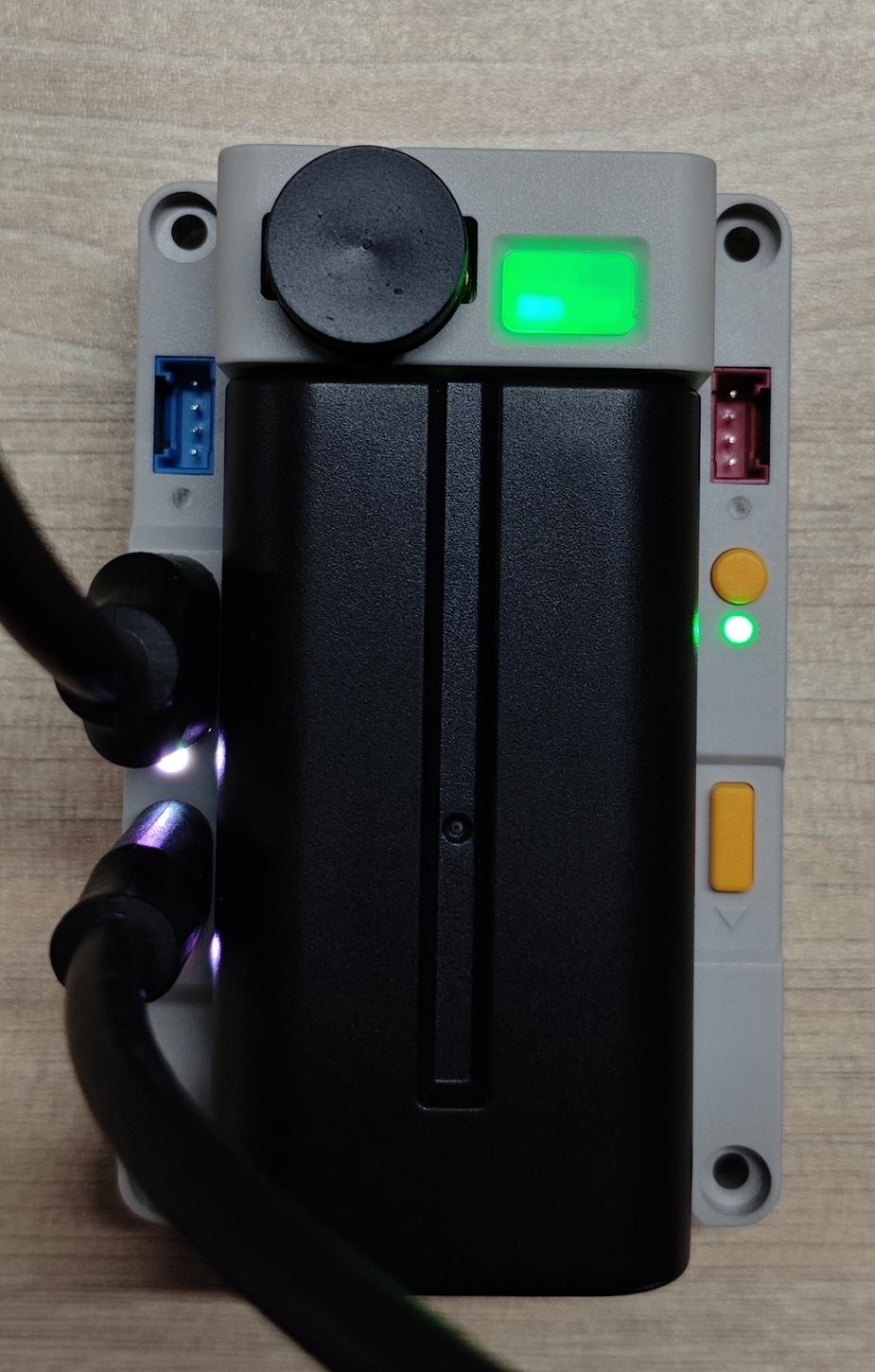
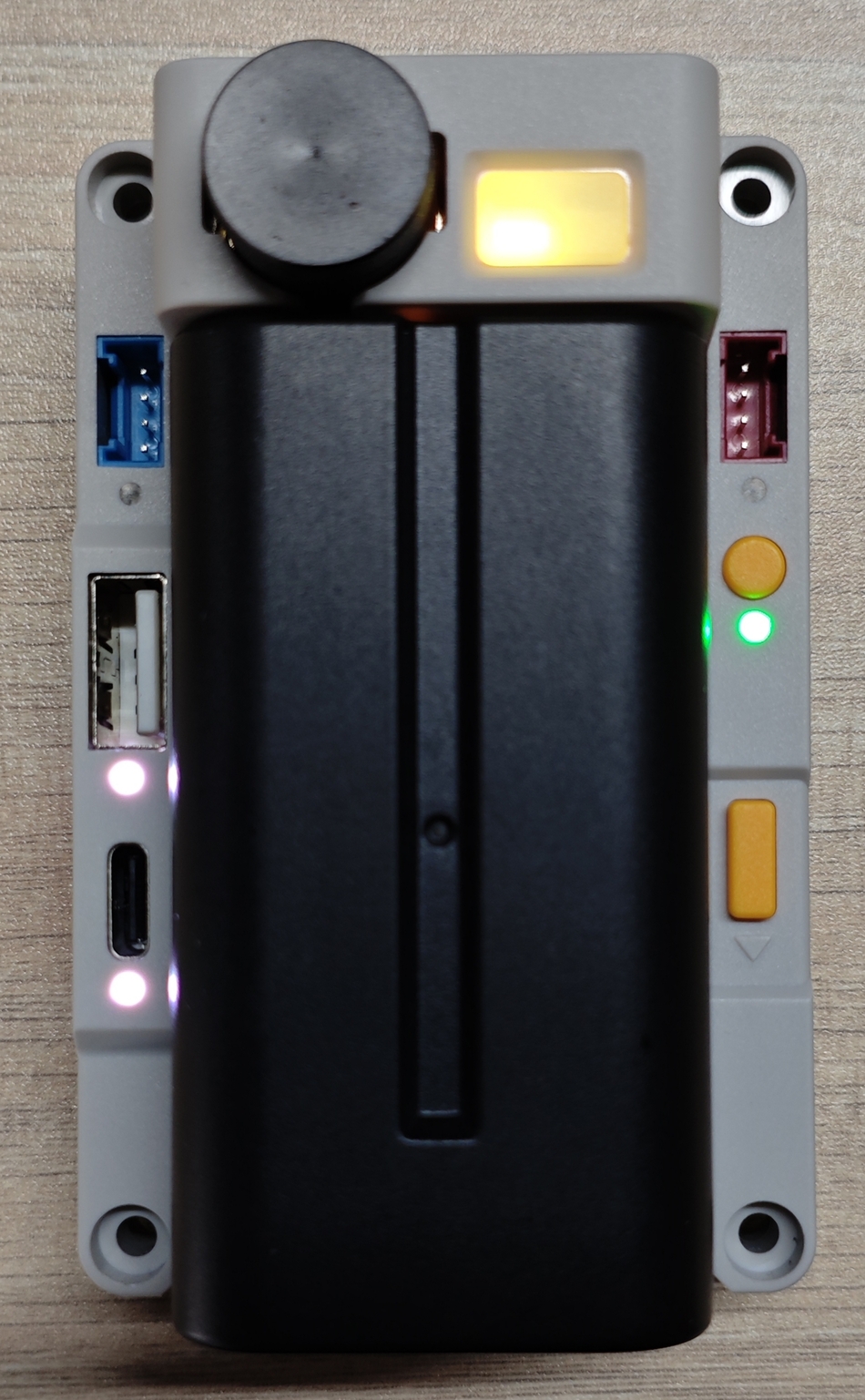
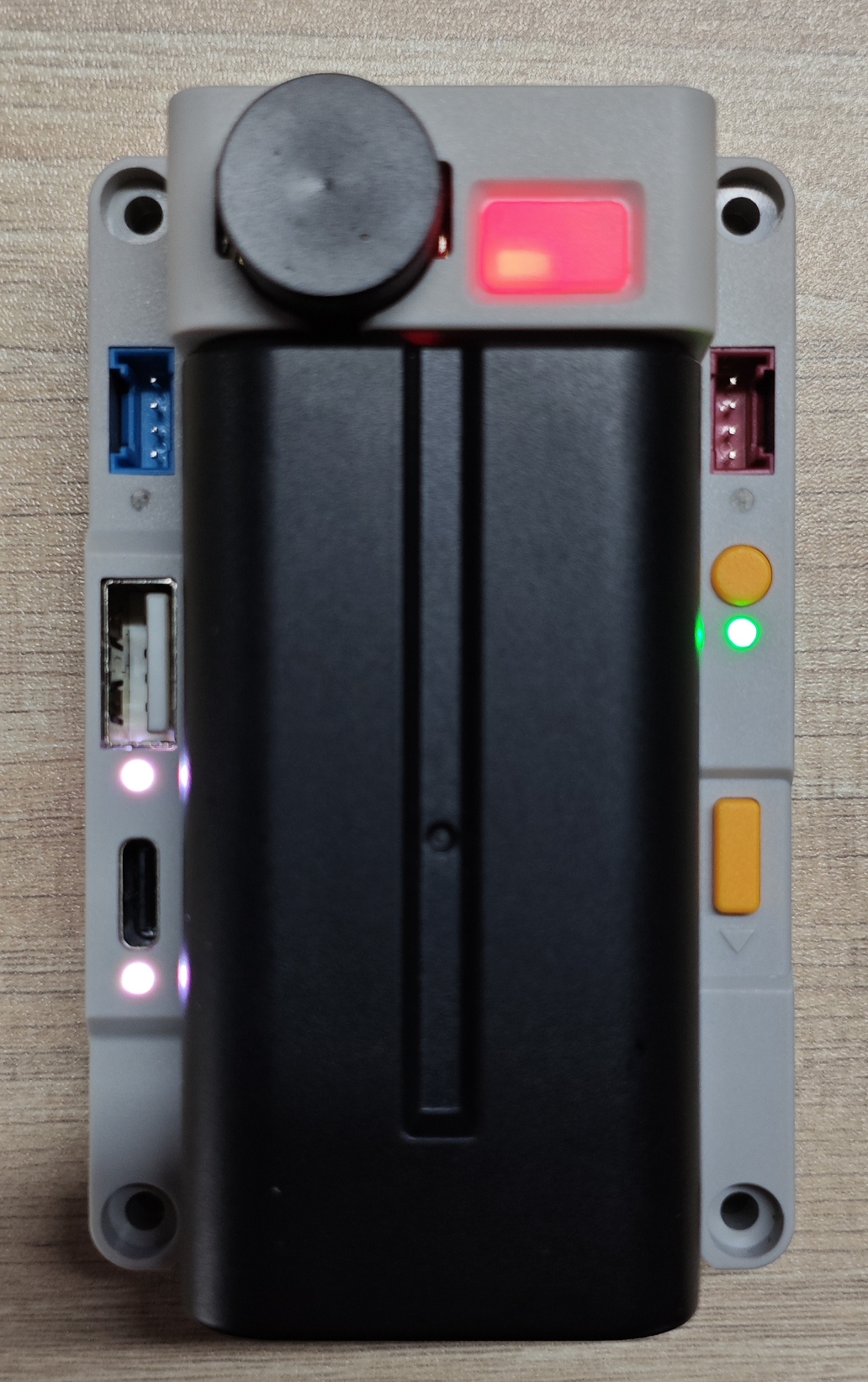
The RGB LED is designed to conveniently indicate the power status of each channel, with the readings of Sensors, you can update your Light component accordingly.
For an example, turn on the LEDs inside the Top PMU button when boot:
esphome:
...
on_boot:
then:
# Turn on the power (L/R) light
# default color is white
- light.turn_on:
id: led_pwr_l
brightness: 100%
- light.turn_on:
id: led_pwr_r
brightness: 100%Update the PMU LEDs when battery level changed:



sensor:
- platform: powerhub
...
battery_level:
name: "Battery Percentage"
id: bat_level_sensor
on_value:
- lambda: |-
auto call_1 = id(led_pwr_l).turn_on();
auto call_2 = id(led_pwr_r).turn_on();
auto call_off_1 = id(led_pwr_l).turn_off();
auto call_off_2 = id(led_pwr_r).turn_off();
call_1.set_transition_length(1000);
call_2.set_transition_length(1000);
call_off_1.set_transition_length(1000);
call_off_2.set_transition_length(1000);
call_1.set_color_mode(ColorMode::RGB);
call_2.set_color_mode(ColorMode::RGB);
// if read battery level is unknown
// set the LED color to white
if ( std::isnan(x) ) {
call_1.set_rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
call_2.set_rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
call_1.set_brightness(1.0);
call_2.set_brightness(1.0);
call_1.perform();
call_2.perform();
return;
}
if ( x > 80.0f && x <= 100.0f ) {
call_1.set_rgb(0, 1.0, 0);
call_2.set_rgb(0, 1.0, 0);
call_1.set_brightness(1.0);
call_2.set_brightness(1.0);
call_1.perform();
call_2.perform();
} else if ( x > 50.0f && x <= 80.0f ) {
call_1.set_rgb(0, 1.0, 0);
call_2.set_rgb(0, 1.0, 0);
call_1.set_brightness(1.0);
call_2.set_brightness(0.8);
call_1.perform();
call_2.perform();
} else if ( x > 20.0f && x <= 50.0f ) {
call_1.set_rgb(1.0, 0.95, 0.19); // left only one LED on with YELLOW color suggest low power
call_1.perform();
call_off_2.perform();
} else if ( x > 5.0f && x <= 20.0f ){
call_1.set_rgb(1.0, 0.43, 0.32); // left only one LED on with RED color suggest extremely low power
call_1.perform();
call_off_2.perform();
} else {
call_1.set_rgb(1.0, 0.43, 0.32);
call_1.set_brightness(0.8); // almost empty
call_1.perform();
call_off_2.perform();
}
...or turn on/off the corresponding LEDs when turn on/off the power switches.
switch:
- platform: powerhub
...
usb_pwr:
name: "USB Power"
id: usb_pwr_switch
on_turn_on:
- light.turn_on:
id: led_usb_a
brightness: 90%
# Color maybe
# red: 100%
# green: 100%
# blue: 100%
- light.turn_on:
id: led_usb_c
brightness: 90%
on_turn_off:
- light.turn_off:
id: led_usb_a
- light.turn_off:
id: led_usb_c
grove_red_pwr:
name: "Port.A Power"
id: grove_red_pwr_switch
on_turn_on:
- light.turn_on:
id: led_grove_red
brightness: 90%
on_turn_off:
- light.turn_off:
id: led_grove_red
grove_blue_pwr:
name: "Port.C Power"
id: grove_blue_pwr_switch
on_turn_on:
- light.turn_on:
id: led_grove_blue
brightness: 90%
on_turn_off:
- light.turn_off:
id: led_grove_blue
rs485_can_pwr:
name: "RS485&CAN Power"
id: rs485_can_pwr_switch
on_turn_on:
- light.turn_on:
id: led_rs485_can
brightness: 90%
on_turn_off:
- light.turn_off:
id: led_rs485_can
charge_pwr:
name: "Charge Power"
id: charge_pwr_switch
restore_mode: RESTORE_DEFAULT_ON
on_turn_on:
- light.turn_on:
id: led_bat_charge
brightness: 90%
on_turn_off:
- light.turn_off:
id: led_bat_charge
...You can also add some special effects to the light, for an example, when battery is charging we use a pulse effect to indicate:
light:
- platform: powerhub
...
bat_charge_rgb:
id: led_bat_charge
name: "Battery Charge Light"
effects:
- pulse:
name: "Slow Pulse"
transition_length: 500ms
update_interval: 2s
...text_sensor:
- platform: powerhub
charge_status:
name: "Battery Charge Status"
id: bat_charge_status_text_sensor
on_value:
- lambda: |-
static std::string last_state = "";
if (last_state == x) return;
last_state = x;
auto call = id(led_bat_charge).turn_on();
call.set_brightness(0.9);
call.set_color_mode(ColorMode::RGB);
if (x == "Charging") {
// Pulse green
call.set_rgb(0, 1.0, 0);
call.set_effect("Slow Pulse");
} else if (x == "Discharging") {
// Solid green
call.set_rgb(0, 1.0, 0);
call.set_effect("None");
} else {
// Solid white
call.set_rgb(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
call.set_effect("None");
}
call.perform();Time
powerhub has a RX8130 RTC chip, which can act as a Time source for the device.
time:
- platform: powerhub
id: powerhub_timeConfiguration variables
- powerhub_id (Optional, ID): The ID to PowerHub.
- All other options from Base Time Configuration
powerhub.write_time Action
This Action triggers a synchronization of the current system time to the RTC hardware.
on_...:
- powerhub.write_time
# in case you need to specify the powerhub id
- powerhub.write_time:
id: powerhub_timepowerhub.read_time Action
This Action triggers a synchronization of the current system time from the RTC hardware.
update_interval can be changed.)This action can be used to trigger additional synchronizations.
on_...:
- powerhub.read_time
# in case you need to specify the powerhub id
- powerhub.read_time:
id: powerhub_timeTime Configuration Example
In a typical setup, you will have at least one additional time source to synchronize the RTC with. Such an external time source might not always be available e.g. due to a limited network connection. In order to have a valid, reliable system time, the system should read the RTC once at start and then try to synchronize with an external reliable time source. When a synchronization to another time source was successful, the RTC can be resynchronized.
esphome:
on_boot:
then:
# read the RTC time once when the system boots
powerhub.read_time:
time:
- platform: powerhub
# repeated synchronization is not necessary unless the external RTC
# is much more accurate than the internal clock
update_interval: never
timezone: America/Los_Angeles # Pacific
# timezone: America/New_York # Eastern
- platform: homeassistant
# instead try to synchronize via network repeatedly ...
on_time_sync:
then:
# ... and update the RTC when the synchronization was successful
powerhub.write_time: