StickS3 Low-Power Configuration
1. Multi-Level Power Switch Design
StickS3 integrates an internal PY32 PMIC. Combined with the hardware circuit design, it implements a multi-level power switch architecture. Different power switch levels control the power supply to corresponding peripherals and interfaces. Users can switch between different power enable levels according to runtime requirements, turning off unused peripherals to achieve overall low power consumption.
M5PM1 Driver Library
Using M5PM1 allows very convenient configuration of the PY32 PMIC pin functions, which can be used for low-power wake-up and peripheral power supply switching.
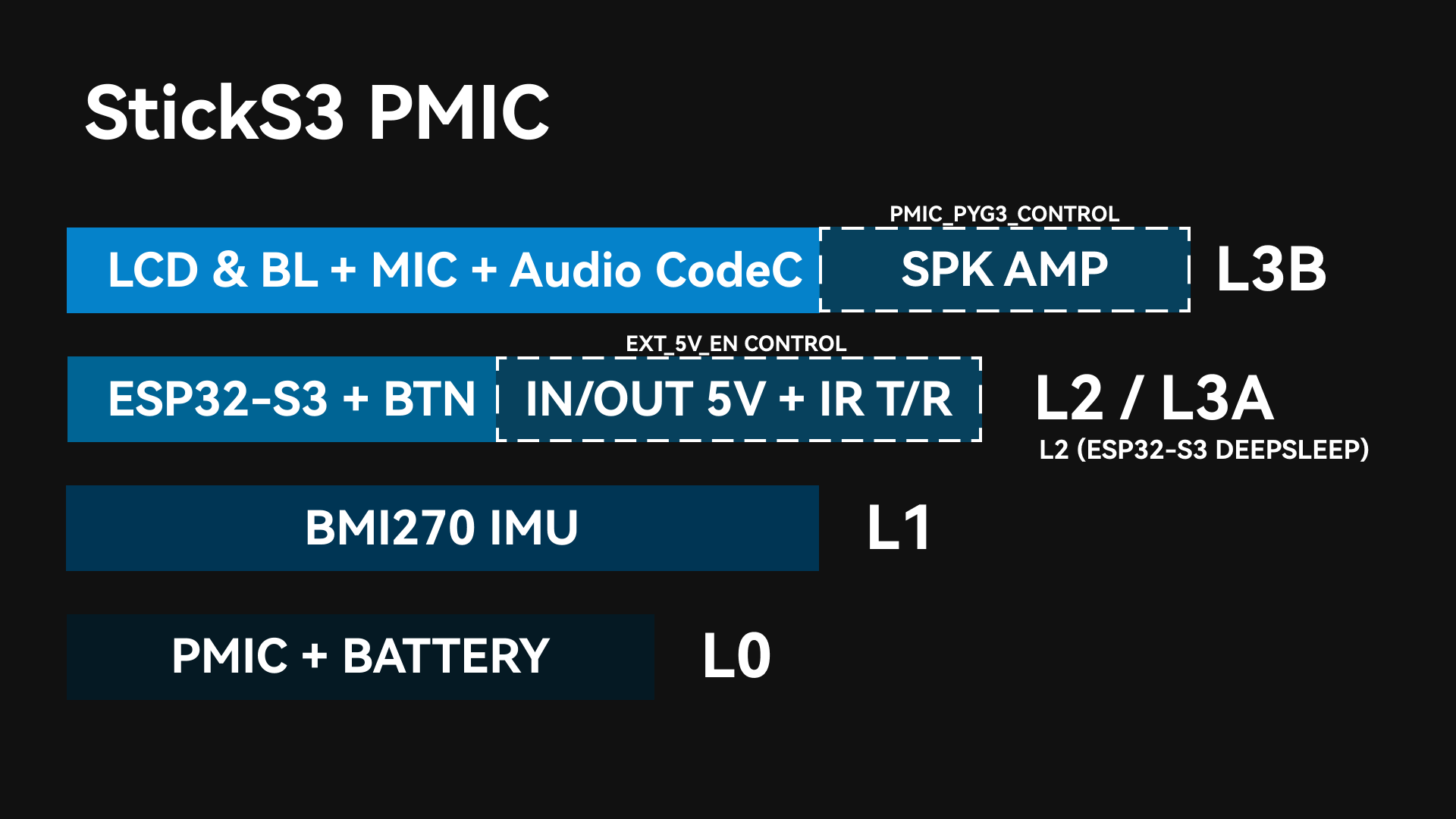
After the PMIC is powered on and started, L0, L1, and L2 will be automatically enabled (with DCDC3V3_EN_PP, LDO3V3_EN_PP, CHG_EN_PP enabled by default). During the M5Unified initialization process, L3A and L3B will be further enabled to power other peripherals.
L0
At this power level, the battery continues to supply power to the PMIC, while other peripherals can have their power turned off. As long as the battery is not depleted, this power level will be maintained. The PMIC supports basic button-based power on/off operations.
L1
Enables power supply to the IMU peripheral. The power switch at this level uses the PMIC’s LDO3V3_EN_PP, which can be controlled via the following API.
pm1.setLdoEnable(true); // L1 ON
pm1.setLdoEnable(false); // L1 OFFAt the same time, the IMU INT1 interrupt pin is connected to the PMIC’s PYG4. By configuring the relevant registers, it is possible to keep the IMU powered while the PMIC enters sleep mode. By flipping the device, the IMU interrupt can be triggered to wake up the PMIC. The following API can be used to keep the IMU (L1) power supply enabled.
pm1.setLdoEnable(true);
pm1.ldoSetPowerHold(true);
pm1.setLedEnLevel(true);
pm1.shutdown();L2/L3A
Enable power supply for the ESP32-S3, expansion interfaces, infrared, and key pull-up sections. When the ESP32-S3 is in sleep mode, the power supply is at Level L2. The ESP32-S3 can turn off L2 by controlling the PMIC to enter sleep mode; when the PMIC triggers wake-up, L2 will be re-enabled.
L3B
This power level turns on all peripheral power supplies, including the LCD backlight, MIC, and SPK. The power switch at this level uses the PMIC’s PYG2, which can be controlled via the following API.
pm1.gpioSetFunc(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_2, M5PM1_GPIO_FUNC_GPIO);
pm1.gpioSetMode(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_2, M5PM1_GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
pm1.gpioSetDrive(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_2, M5PM1_GPIO_DRIVE_PUSHPULL);
pm1.gpioSetOutput(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_2, false);EXT_5V_EN
In the default M5Unified initialization, EXT_5V_EN is disabled (the output of the Grove and Hat EXT_5V interfaces is turned off, switching them to input mode). You can switch between input and output via the following API.
M5.Power.setExtOutput(true); // EXT_5V OUTPUT
M5.Power.setExtOutput(false); // EXT_5V INPUT2. PMIC Sleep
Manual Sleep
The PMIC can be manually controlled by software to enter sleep mode, reducing overall power consumption. By default, directly entering sleep will fall back to the L0 power level, where only the PMIC remains powered.
In some special use cases (such as IMU wake-up or ESP32-S3 SoC sleep), it is allowed for the PMIC to enter sleep mode while keeping certain peripheral power levels enabled, serving as wake-up sources or for state retention.
Such applications require configuring the power switch pin states of the corresponding levels and enabling state retention before the PMIC enters sleep mode.
I2C Idle Sleep
The PMIC supports configuring automatic sleep during I2C idle communication to reduce overall power consumption. After entering sleep mode, the first communication between the ESP32-S3 and the PMIC will be used to wake up the PMIC and will therefore fail. Effective communication will occur on the subsequent transaction after wake-up.
3. IMU Example Programs
Example program PlatformIO source project file:
IMU PMIC Wake-Up
The power is switched to L1 mode, where only the IMU and PMIC are powered. After configuring the IMU wake-up function, the PMIC also enters sleep mode while keeping the L1 output power (3V3_L1_EN) enabled to maintain IMU operation.
At this point, flipping or moving the device can trigger the IMU wake-up signal, waking the PMIC and restarting the system.
After the PMIC wakes up, it will re-run the L0, L1, and L2 power-on sequence. The ESP32-S3 will re-execute initialization.
Example description: After the device is powered on, press Button A once to configure the IMU interrupt mode and PMIC L1 power hold, then the PMIC enters sleep. Flipping or moving the device will trigger PMIC wake-up, and the ESP32-S3 will be powered on again.
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5PM1.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "./bmi270/src/bmi270.h"
static BMI270_Class* bmi270 = nullptr;
M5PM1 pm1;
void setup(void)
{
M5.begin();
M5.Display.setRotation(1);
Serial.begin(115200);
auto pin_num_sda = M5.getPin(m5::pin_name_t::in_i2c_sda);
auto pin_num_scl = M5.getPin(m5::pin_name_t::in_i2c_scl);
M5_LOGI("getPin: SDA:%u SCL:%u", pin_num_sda, pin_num_scl);
Wire.end();
Wire.begin(pin_num_sda, pin_num_scl, 100000U);
// Initialize PM1
m5pm1_err_t err = pm1.begin(&Wire, M5PM1_DEFAULT_ADDR, pin_num_sda, pin_num_scl, M5PM1_I2C_FREQ_100K);
if (err == M5PM1_OK) {
Serial.println("PM1 initialization successful");
pm1.gpioSetWakeEnable(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_4, true);
pm1.gpioSetWakeEdge(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_4, M5PM1_GPIO_WAKE_FALLING); // Falling edge
} else {
Serial.printf("PM1 initialization failed, error code: %d\n", err);
}
// Initialize BMI270
bmi270 = new BMI270_Class();
bmi270->setWire(&Wire);
if (bmi270->init()) {
Serial.println("BMI270 initialization successful");
M5.Display.fillScreen(BLACK);
M5.Display.setTextSize(2);
M5.Display.setTextColor(WHITE);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 10);
M5.Display.println("IMU Wakeup Test");
M5.Display.println("Press BtnA to Sleep");
M5.Display.println("Shake to wake up");
} else {
Serial.println("BMI270 initialization failed");
delete bmi270;
bmi270 = nullptr;
}
}
void loop(void)
{
M5.update();
if (M5.BtnA.wasPressed()) {
// Configure BMI270 any motion interrupt
if (bmi270 != nullptr) {
if (bmi270->enableAnyMotionInterrupt(0xA0, 0x0A)) {
Serial.println("BMI270 AnyMotionInterrupt enabled successfully");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to enable BMI270 AnyMotionInterrupt");
}
} else {
Serial.println("BMI270 not initialized");
}
M5.Display.fillScreen(BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 10);
M5.Display.println("Power OFF");
delay(1000);
// Shutdown
pm1.setLdoEnable(true);
pm1.ldoSetPowerHold(true);
pm1.setLedEnLevel(true);
pm1.shutdown();
}
}IMU ESP32-S3 Wake-Up
The PMIC’s PYG1_IRQ pin is electrically connected to G13 of the ESP32-S3. ESP32-S3 wake-up can be achieved through chained wake-up signals. The steps are as follows:
- Configure PMIC PYG4 as input mode. This pin is connected to the IMU INT1 output signal.
- Configure PMIC PYG1_IRQ as an IRQ output pin. When the PYG4 (IMU interrupt signal) pin state changes, the PYG1_IRQ pin will output a signal.
- Configure the ESP32-S3 to enter sleep mode and set the wake-up pin to G13.
- Flip or move the device: trigger IMU wake-up signal -> trigger PMIC PYG1_IRQ -> wake up ESP32-S3.
Example description: After the device is powered on, press Button A once to configure the IMU interrupt mode. Flipping or moving the device will trigger the GPIO interrupt handler. Press Button A again to clear the PMIC IRQ flag and test again.
#include <M5Unified.h>
#include <M5PM1.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "./bmi270/src/bmi270.h"
#include "driver/rtc_io.h"
static BMI270_Class* bmi270 = nullptr;
M5PM1 pm1;
void setup(void)
{
M5.begin();
M5.Display.setRotation(1);
Serial.begin(115200);
auto pin_num_sda = M5.getPin(m5::pin_name_t::in_i2c_sda);
auto pin_num_scl = M5.getPin(m5::pin_name_t::in_i2c_scl);
M5_LOGI("getPin: SDA:%u SCL:%u", pin_num_sda, pin_num_scl);
// Initialize PM1
m5pm1_err_t err = pm1.begin(&Wire, M5PM1_DEFAULT_ADDR, pin_num_sda, pin_num_scl, M5PM1_I2C_FREQ_100K);
if (err == M5PM1_OK) {
Serial.println("PM1 initialization successful");
pm1.irqClearGpioAll();
pm1.irqClearSysAll();
pm1.irqClearBtnAll();
pm1.irqSetGpioMaskAll(M5PM1_IRQ_MASK_ENABLE);
pm1.irqSetSysMaskAll(M5PM1_IRQ_MASK_ENABLE);
pm1.irqSetBtnMaskAll(M5PM1_IRQ_MASK_ENABLE);
pm1.irqSetGpioMask(M5PM1_IRQ_GPIO4, M5PM1_IRQ_MASK_DISABLE);
pm1.gpioSetMode(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_4, M5PM1_GPIO_MODE_INPUT);
pm1.gpioSetPull(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_4, M5PM1_GPIO_PULL_UP);
pm1.gpioSetMode(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_1, M5PM1_GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
pm1.gpioSetDrive(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_1, M5PM1_GPIO_DRIVE_PUSHPULL);
pm1.gpioSetFunc(M5PM1_GPIO_NUM_1, M5PM1_GPIO_FUNC_IRQ);
} else {
Serial.printf("PM1 initialization failed, error code: %d\n", err);
}
// Initialize BMI270
bmi270 = new BMI270_Class();
bmi270->setWire(&Wire);
if (bmi270->init()) {
Serial.println("BMI270 initialization successful");
M5.Display.fillScreen(BLACK);
M5.Display.setTextSize(2);
M5.Display.setTextColor(WHITE);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 10);
M5.Display.println("IMU IRQ Test");
M5.Display.println("Press BtnA to Setup");
M5.Display.println("Then Shake");
} else {
Serial.println("BMI270 initialization failed");
delete bmi270;
bmi270 = nullptr;
}
}
void ARDUINO_ISR_ATTR pm1_irq_handler()
{
Serial.println("PM1 IRQ triggered");
M5.Display.println("PM1 IRQ triggered");
}
void loop(void)
{
M5.update();
if (M5.BtnA.wasPressed()) {
pm1.irqClearGpioAll();
pm1.irqClearSysAll();
pm1.irqClearBtnAll();
// Configure BMI270 any motion interrupt
if (bmi270 != nullptr) {
if (bmi270->enableAnyMotionInterrupt(0xA0, 0x0A)) {
Serial.println("BMI270 AnyMotionInterrupt enabled successfully");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to enable BMI270 AnyMotionInterrupt");
}
} else {
Serial.println("BMI270 not initialized");
}
M5.Display.fillScreen(BLACK);
M5.Display.setCursor(0, 10);
M5.Display.println("Now Shake!");
pinMode(GPIO_NUM_13, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(GPIO_NUM_13, pm1_irq_handler, FALLING);
// esp_sleep_enable_ext0_wakeup(GPIO_NUM_13, 0); // 0 = Low
// rtc_gpio_pullup_en(GPIO_NUM_13);
// Serial.println("Going to sleep now");
// esp_deep_sleep_start();
}
}